Trisomy 13 or Patau Syndrome is the most severe viable trisomy caused by an additional copy of chromosome 13 that usually causes a host of developmental problems and physical deformities in a newborn. Patau syndrome is generally recognized at birth by the presence of structural birth defects and poor neurologic performance.
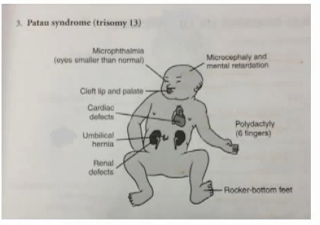
Additional structural anomalies are common, particularly facial anomalies (midline clefts, hypotelorism, microphthalmia, and anophthalmia) arising from structural anomalies of the brain, frequently microcephaly and holoprosencephaly. Other associated anomalies include cardiac, renal, and intestinal (diaphragmatic hernia) anomalies. Characteristic features include low set ears, post-axial polydactyly, flexion contractures, rocker bottom feet, scalp defects, and haemangiomas.
What is the cause of Patau Syndrome ?
The exact incidence of Patau syndrome is not known, although it appears to affect females more than males, most likely because male fetuses do not survive until birth. Patau syndrome, like Down syndrome, is associated with increased age of the mother. It may affect individuals of all ethnic backgrounds.
Most cases of Patau syndrome are not inherited, but occur as random events during the formation of reproductive cells (eggs and sperm). An error in cell division called non-disjunction can result in reproductive cells with an abnormal number of chromosomes. For example, an egg or sperm cell may gain an extra copy of the chromosome. If one of these atypical reproductive cells contributes to the genetic makeup of a child, the child will have an extra chromosome 13 in each of the body's cells. Mosaic Patau syndrome is also not inherited. It occurs as a random error during cell division early in fetal development.
Look the video of Patau Syndrome
POSTNATAL
There is a high rate of attrition of affected pregnancies and many abort spontaneously. Trisomy 13 is reported to be as common in spontaneous abortions as trisomy 18. Most affected live born infants die within the first weeks of life. Some cases with mosaic trisomies have survived for several years, all affected by severe mental retardation.
Treatment of Trisomy 13 / Patau Syndrome
Treatment of Patau syndrome focuses on the particular physical problems with which each child is born. Many infants have difficulty surviving the first few days or weeks due to severe neurological problems or complex heart defects. Surgery may be necessary to repair heart defects or cleft lip and cleft palate. Physical, occupational, and speech therapy will help individuals with Patau syndrome reach their full developmental potential.

Comments
Post a Comment